Angular 2.0 with extensive features dominates the World Web
Angular 2.0 has attested widespread domination in Open Source JavaScript Frameworks and it is highly appreciated amongst developers and enterprises for its high functioning solutions. Angular 2.0, an advanced client-side MVW framework, is highly adopted nowadays for mobile app and web app development.

Major Blocks of Angular 2.0
Developers for Angular 2.0 application development uses Typescript as a primary language with support of ECMAScript 6 standardization. Typescript is basically a compiled type language with a strongly typed layer in conjunction with JavaScript. Typescript allows to write a class, interface, and module statements just like in Java or C# which boosts the performance of web and mobile solution as the code written in Typescript are less inclined to run-time errors. Below is mentioned for the major 8 blocks of Angular 2.0 architecture:
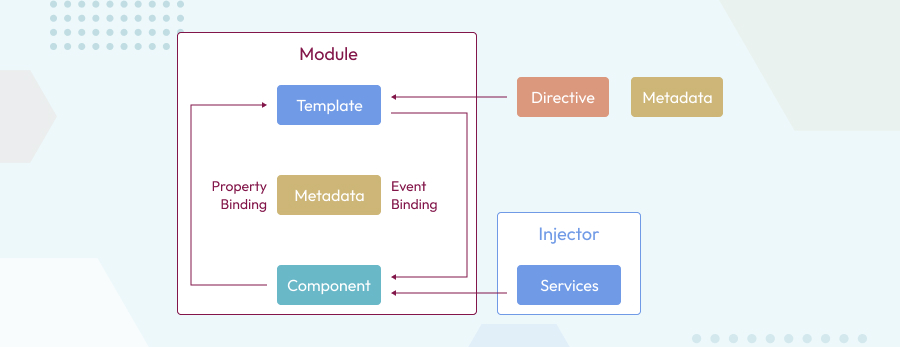
- Module – Module is very similar to a class. A module can be described by a block of code which is used to perform a particular single task. Angular 2.0 has a feature of modularity, where a single application is built by separating it in many modules. Export statement is used to export component class from a module.
- Component – View of the application and logic on the page and on click execution depends upon the component as it is a core part of the code and it belongs to the controller class. @Component is used to register a component and only one component is used per DOM element. Also, CSS styles can be connected with a component using inline styles, style URLs and template inline styles.
- Template – Template is the main part which justifies the look of the component. It can be said that the view of the component is defined using the template. To display value, add template expression in code.
- Metadata – Metadata is majorly used to extend the functionality of the class. In Typescript, for this purpose is defined by decorate class. For example, to define any component in an Angular application, use metadata of the class (i.e. @Component decorator).
- Data Binding – The most powerful feature, Data Binding, is the connection bridge between Model and View. It gets automatically synchronized. Angular 2.0 supports four types of binding – Property Binding, Event Binding, Interpolation, and Two-Way Binding.
- Directive – Directives are custom HTML attributes used to prolong the power of HTML. To create a directive, the @Directive decorator is applied on connected metadata of the class. Three types of directives – Decorator, Component and Template.
- Services – Services are used when a single functionality is used commonly in various modules of the application. Basically, is used to share the data and behavior within the application. Service has no base class. Commonly used services are logging service, data service, message service, etc.
- Dependency Injection – To attach the functionality of components at runtime, dependency injection is used. As objects are passed as dependencies, it makes dependencies configurable – removing its hard-coded dependencies. With dependency injection, components can be easily maintainable, reusable and testable.
export class AppComponent { } |
<div> Your name is : {{name}} </div> |
Benefits of Angular 2.0 App Development
Angular 2.0 efficiently met the great expectations of developers and enterprises by catering them a solution having comprehensive advantages.
- Along with mobile-driven, Angular JS also provide wide-ranging cross-platform support for desktop apps on Windows, Linux, and Mac.
- With Command Line Integration, Angular 2.0 provides higher speed and impeccable performance in terms of browser rendering, testing, animation, faster code generation and accessibility across all the components.
- Supports Automated Unit Testing
- Router Strengthening allows apps to load rapidly for delivering automatic code-splitting.
- Modularization loads only the view which is requested, which in turn decreases the load and boosts the performance.
- Supports AOT (Ahead-of-Time). With AOT, the compiler runs once at build time using a set of libraries. It even downloads pre-compiled version of an application for faster rendering.
- As it is component/class based, its maintenance is very easy.
- Can create complex choreographies and animation timelines with simple and less code via Angular’s intuitive API.
- HTML 5 is supported
- Paves way for Search Engine Optimization
Comparison
Along with bug fixes and enhancements in Angular 1.x, Google also came up with cutting edge changes in Angular 2.0 Right from architecture to the typing script is changed in Angular 2. Have a look on a basic comparison of Angular 1.x and Angular 2.0.
| Attribute | Angular 1.x | Angular 2.0 |
| Modular Architecture | Yes | Improved |
| Performance | Web-centric (Native Mobile Support) | Mobile centric |
| Rendering | Client side | Server side |
| Script | JavaScript | Typescript, JavaScript and Dart |
| Standard | MVC based | Component, MVVM based |
| Npm(Node Package Manager) | Not needed | Required |
| Setup | Easy to setup | Complicated (depends on 3rd party library) |
| Hierarchical Dependency Injection | Not supported | Supported |
| Package Manager & Runtime server | Not required | Both required |
Conclusion
Angular 2.0 is the future of development as it is the platform which has something worthwhile for every developers and business solutions desires. Angular 2.0 indeed changed the World of Web. This year, in 2017, Google completely surprised ecosystem by skipping Angular 3. Google came up with Angular 4 with no drastic changes in Angular 2.0, apart by important bug fixes, minor changes in core libraries and necessary enhancement.
Angular 1.x is a JavaScript based open-source front end web application framework, backed by Google. It is a powerful light weight JavaScript framework used to...
 Jun 21, 2017
Jun 21, 2017 



Comments
Leave a message...